Posts Tagged ‘collada’
This Part of the Shaders Tutorial series will show you how to add Phong vshader to either a dae imported object or to a basic primitive.
If you are a novice, it is advised that you follow this tutorial from the initial section that can be found here, which explains how to set up the files and the scene. Otherwise please read on.
For those following on the shaders tutorial series, i will be calling this .as file phongMat
package phongMat {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
import flash.text.TextField;
import flash.text.TextFormat;
import org.papervision3d.cameras.CameraType;
import org.papervision3d.lights.PointLight3D;
import org.papervision3d.materials.shadematerials.PhongMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.materials.utils.MaterialsList;
import org.papervision3d.objects.primitives.Sphere;
import org.papervision3d.render.BasicRenderEngine;
import org.papervision3d.view.BasicView;
import org.papervision3d.objects.parsers.DAE;
import org.papervision3d.objects.DisplayObject3D;
public class phongMat extends Sprite
{
This Part of the Shaders Tutorial series will show you how to add Flat shader material to either a dae imported object or to a basic primitive.
If you are a novice, it is advised that you follow this tutorial from the initial section that can be found here, which explains how to set up the files and the scene. Otherwise please read on.
For those following on the shaders tutorial series, i will be calling this .as file flatMat
to begin with we must begin the package and import the relevant classes
package flatMat {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
import flash.text.TextField;
import flash.text.TextFormat;
import org.papervision3d.cameras.CameraType;
import org.papervision3d.lights.PointLight3D;
import org.papervision3d.materials.shadematerials.FlatShadeMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.materials.shadematerials.CellMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.materials.utils.MaterialsList;
import org.papervision3d.objects.primitives.Sphere;
import org.papervision3d.render.BasicRenderEngine;
import org.papervision3d.view.BasicView;
import org.papervision3d.objects.parsers.DAE;
import org.papervision3d.objects.DisplayObject3D;
now we must begin the class, and add the variables that we will be using
This Part of the Shaders Tutorial series will show you how to add colorMaterial shader to either a dae imported object or to a basic primitive.

Colour Material Shader Example
If you are a novice, it is advised that you follow this tutorial from the initial section that can be found here, which explains how to set up the files and the scene. Otherwise please read on.
This code is pretty basic / self explanatory, so I will not be explaining much about it. If you do require any help, just post a comment below.
package colorMat {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
import flash.text.TextField;
import flash.text.TextFormat;
import org.papervision3d.cameras.CameraType;
import org.papervision3d.materials.ColorMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.materials.utils.MaterialsList;
import org.papervision3d.objects.primitives.Sphere;
import org.papervision3d.render.BasicRenderEngine;
import org.papervision3d.view.BasicView;
import org.papervision3d.objects.parsers.DAE;
import org.papervision3d.objects.DisplayObject3D;
public class colorMat extends Sprite
{
private var view:BasicView;
private var color:ColorMaterial;
private var sphere:Sphere;
private var tf:TextField;
private var format:TextFormat;
private var dae:DAE;
private var daeFile:String;
private var daeMaterialName:String;
This Part of the Shaders Tutorial series will show you how to add an Environmental Material Shader to your objects.
What this basically does is take a texture imported from the background and use it to reflect off the object, giving the object a highly reflective coating which is faked. This keeps processing power down, while giving a nice effect.
For this tutorial we will be creating an effect that looks something like this: (please be patient while the video loads)
If you are a novice, it is advised that you follow this tutorial from the initial section that can be found here, which explains how to set up the files and the scene. Otherwise please read on.
To begin with, we must begin our new package and import our classes.
package environmentMat{
import flash.display.BitmapData;
import flash.display.Loader;
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
import flash.net.URLRequest;
import flash.text.TextField;
import flash.text.TextFormat;
import org.papervision3d.cameras.CameraType;
import org.papervision3d.lights.PointLight3D;
import org.papervision3d.materials.shadematerials.EnvMapMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.objects.primitives.Sphere;
import org.papervision3d.render.BasicRenderEngine;
import org.papervision3d.view.BasicView;
//
import org.papervision3d.objects.parsers.DAE;
import org.papervision3d.objects.DisplayObject3D;
//Ability to add materials
import org.papervision3d.materials.BitmapMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.materials.BitmapFileMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.materials.utils.MaterialsList;
Then initialise our class and create the variables that will be using
public class environmentMat extends Sprite {
private var view:BasicView;
private var img:Loader;
private var environment:EnvMapMaterial;
private var light:PointLight3D;
private var sphere:Sphere;
private var angle:Number = new Number(0);
private var tf:TextField;
private var format:TextFormat;
private var dae:DAE;
private var daeFile:String;
private var daeMaterialName:String;
For one of the most basic shader examples, we will be learning about the Composite Shader, this basicaly gives your object a solid color with wireframe showing.
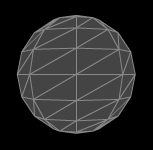
Composite Material Example
If you are a beginner to PV3D/Flash, My examples will be working from my initial post on Shaders which can be found here.
Otherwise please feel free to continue.
Firstly we will need to import all necessary classes
package compositeMat {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
import flash.text.TextField;
import flash.text.TextFormat;
import org.papervision3d.cameras.CameraType;
import org.papervision3d.materials.ColorMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.materials.WireframeMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.materials.special.CompositeMaterial;
import org.papervision3d.materials.utils.MaterialsList;
import org.papervision3d.objects.primitives.Sphere;
import org.papervision3d.render.BasicRenderEngine;
import org.papervision3d.view.BasicView;
import org.papervision3d.objects.parsers.DAE;
import org.papervision3d.objects.DisplayObject3D;
Next we will pass the class, and the variables that we will be using
public class compositeMat extends Sprite
{
private var view:BasicView;
private var color:ColorMaterial;
private var wire:WireframeMaterial;
private var composite:CompositeMaterial;
private var sphere:Sphere;
private var tf:TextField;
private var format:TextFormat;
private var dae:DAE;
private var daeFile:String;
private var daeMaterialName:String;
And we will now finish off with our functions
public function compositeMat()
{
//controls camera size initialises BasicView
view = new BasicView(300, 300, false, false, CameraType.FREE);
//Sets up Rendering Engine
view.renderer = new BasicRenderEngine(); addChild(view);
//Select colours for Wireframe and object
color = new ColorMaterial(0x444444);
wire = new WireframeMaterial(0x888888);
composite = new CompositeMaterial();
composite.addMaterial(color);
composite.addMaterial(wire);
//Loading your .dae File
daeFile = "yourdaeFileName.dae";
dae = new DAE();
//adding the composite shader ontop of your DAE model
dae.load(daeFile, new MaterialsList ( { all:composite } ));
//sometimes object needs to be scaled
dae.scale = 100;
//adding the object to the scene
view.scene.addChild(dae);
//Formating and adding text label to the scene.
format = new TextFormat("Arial", 10, 0xFFFFFF);
tf = new TextField(); tf.width = 230; tf.text = "Composite Material Shader";
tf.x = 10; tf.y = 10; tf.setTextFormat(format);
addChild(tf);
addEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME, onRenderViewport);
}
private function onRenderViewport(e:Event):void
{
//If you want your object to rotate on its axis
dae.rotationY++;
//Finaly render
view.singleRender();
}
Now if you are following this example on from my Introductory post on Shaders, you will need to import this .as file into you MainShader.as file by typing in the following:
package {
import org.papervision3d.render.BasicRenderEngine;
import org.papervision3d.view.BasicView;
import compositeMat.compositeMat; //IMPORTANT importing the Shader AS file
import flash.display.Sprite;
[SWF (width="800", height="600", framerate="25", backgroundColor="0x333333")];
public class MainShader extends Sprite {
private var composite:compositeMat;
public function MainShader() {
composite = new compositeMat();
addChild(composite);
}
}
}
Now that you have imported your compositeMat.as file into you MainShader.as file, which is linked to whateveryoucallyourFLA.fla file you can press ctrl + shift + Enter to compile and debug your code or
ctrl + Enter to run your movie.
If you enjoyed this tutorial, why not Subscribe to my RSS feeds for all the latest updates on this blog, or use the Share buttons below!



